Mail Server: -
Building a Mail Server on Linux Machine using different packages that separately handle SMTP, POP and IMAP. Where you can manage entire things including package installation configuration etc.Our Goal: -
- Postfix: sends and receives mail via the SMTP protocol. It will only relay mail on to other mail servers if the email is sent by an authenticated user, but anyone can send mail to this server for local delivery.
- Dovecot: A POP and IMAP server that manages local mail directories and allows users to log in and download their mail. It also handles user authentication.
- Postgrey: Greylists incoming mail, requiring unfamiliar deliverers to wait for a while and then resend. This is one of the better tools for cutting down on spam.
- Amavisd-new: a manager for organising various antivirus and spam checking content filters
- Clam Antivirus: A better tool to Scan Emails
- SpamAssassin: for sniffing out spam in emails.
- Postfix Admin: A good web interface to manage Domain, Mailbox, Alias etc.
- RoundCube: A web mail client tool.
Install and Configure E-mail server:
Step 1: - DNS Change
You have to set up your DNS with an A record that points to your mail server IP and an MX record that points to the mail servers hostname.
A tony.in 192.168.102.10
MX mail.tony.in 192.168.102.10
Step 2: - Setup Hostname
We need to setup hostname
hostname mail.tony.in
echo "mail.tony.in" /etc/hostname
127.0.0.1 mail.tony.in mail
Step 3: - Install LAMP Web Server:
We need LAMP server to handle PostfixAdmin web interface and to manage RoundCube web based email client.
3A- Install Apache:-
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install apache2
3B- Install MySQL:
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install mysql-client mysql-server php-mysql
After installing Mysql let's perform post installation task, run mysql_secure_installlation command to setup initial setting.
root@mail:/home/amar# mysql_secure_installation
Press enter button when ask for current password and follow the instruction for other changes you may require.
3C- Install PHP:
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install php7.0 php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-mbstring php-apcu libapache2-mod-php7.0
Step 4: - Allow required Port through Firewall
We need to allow following ports in the firewall to communicate our server with the world.
- 80 (HTTP)
- 25 (SMTP)
- 110 (POP3)
- 143 (IMAP)
- 465 (SMTPS)
- 993 (IMAPS)
- 995 (POPS)
Step 5: - Install Mail server
Please run the command below to install postfix and enter hostname mail.tony.in during installation process when asked.
5A- Postfix Install
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install postfix postfix-mysql
5B- DoveCot Install
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install dovecot-core dovecot-mysql dovecot-imapd dovecot-pop3d
5C- Install all other packages including postgrey, ClamAV Antivirus and SpamAssassin
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install \
> postgrey \
> amavis \
> clamav \
> clamav-daemon \
> spamassassin \
> libdbi-perl \
> libdbd-mysql-perl \
> php7.0-imap \
> postfix-policyd-spf-python
5D- Next, we need to install few optional packages that extend the abilities of the spam and virus detection, Use the command below.
root@mail:/home/amar# apt install \
> pyzor \
> razor \
> arj \
> cabextract \
> lzop \
> nomarch \
> p7zip-full \
> ripole \
> rpm2cpio \
> tnef \
> unzip \
> unrar-free \
> zip \
> zoo
5E- Use OpenSSL to Create a Unique Diffie-Helman Group
openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/private/dhparams.pem 2048
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/dhparams.pem
Step 6: - Configure MySQL
A few alterations to the default MySQL configuration in /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf are needed. Add the following:
A few alterations to the default MySQL configuration in /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf are needed. Add the following:
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
6A- Append following line save file and restart MySQL service.
user = mysql pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock port = 3306 basedir = /usr datadir = /var/lib/mysql tmpdir = /tmp lc-messages-dir = /usr/share/mysql sql_mode=ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
6B- Create a database:
Use command below to create a database and assign permission
root@mail:/home/amar# mysql -u root -p Enter password: ******* MariaDB [(none)]> create database mail; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on mail.* to 'mail'@'localhost' identified by 'mailpassword'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
6C- Now Restart MySQL service
root@mail:/home/amar# systemctl restart mysql
Step 7: - Install and Configure Postfix Admin:
Postfix Admin is installed as follows. To start things off, download the package from Sourceforge, unpack it, move it into a subdirectory of your webroot, and change ownership to the www-data user:root@mail:/home/amar# wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/postfixadmin/postfixadmin/postfixadmin-3.0.2/postfixadmin-3.0.2.tar.gz
root@mail:/home/amar# tar -xf postfixadmin-3.0.2.tar.gz
root@mail:/home/amar# rm -f postfixadmin-3.0.2.tar.gz
root@mail:/home/amar# mv postfixadmin-3.0.2 /var/www/html/postfixadmin
root@mail:/home/amar# chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/postfixadmin
7A- Let's make the changes into config.inc.php
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /var/www/html/postfixadmin/config.inc.php
Make the highlighted changes in the config.inc.php
<?php
// Configuration options here override those in config.inc.php.
// You have to set $CONF['configured'] = true; before the
// application will run.
$CONF['configured'] = true;
// Database connection details.
$CONF['database_type'] = 'mysqli';
$CONF['database_host'] = 'localhost';
$CONF['database_user'] = 'mail';
$CONF['database_password'] = 'mailpassword';
$CONF['database_name'] = 'mail';
// Site Admin
// Define the Site Admin's email address below.
// This will be used to send emails from to create mailboxes and
// from Send Email / Broadcast message pages.
// Leave blank to send email from the logged-in Admin's Email address.
$CONF['admin_email'] = '';
Save and Exit from File7B- Now start browser and open this URL: http://mail.tony.in/postfixadmin/setup.php
Troubleshooting: -You may get error:- Invalid query: Specified key was too long; max key length is 1000 bytes
7C- To fix above error we need to make changes into upgrade.php file
Open upgrade.php file using vi editor.
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /var/www/html/postfixadmin/upgrade.php
type syntax below and hit enter- :%s/255/100/g it find word 500 in the file and replace it with 100
7D- After making change in the file refresh url, if things goes weill you get output as follow
7E- Now enter Setup password, what ever you need and it will give us Hash password that we need to save in config.inc.php file
7F- Open confi.inc.php and add this hash password in front of $conf['setup_password'] line as below
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /var/www/html/postfixadmin/config.inc.php
$CONF['setup_password'] = '29bef8ab87cb037af7efb8257a116469:e05ed5e6eecfa387324c4ba30f40e4d316a77685';
Save and Exit from the file.7G- Create PostfixAdmin superAdmin login account
Super Admin account has been setup successfully.
Troubleshooting: - You may get an error "Admin is not a valid email address!Email address" during admin account setup
This error will occur when our domain is not getting resolved, To solve it let's make and change in config.inc.php file
Open config.inc.php file and change line as below
$CONF['emailcheck_resolve_domain']='NO'
Save and Exit from file.Step 8: - Create Domain and add mailbox:
Let's Use created an admin user to login into postfix admin console:
User- admin@tony.in
password- created password above
8A- Add Domain:
Let's add domain using steps below
8B- Add Domain: Add User mailbox
Follow the steps 1 -8 to add mailbox
One mailbox with name chinu@tony.in has been added successfully.
Step 8: - Create a User to Handle Virtual Mail Directories
We need a User account who can handle Virtual mail directories, So let's create a user using the command below:
root@mail:/home/amar# useradd -r -u 150 -g mail -d /var/vmail -s /sbin/nologin -c "Virtual maildir handler" vmail root@mail:/home/amar# mkdir /var/vmail root@mail:/home/amar# chmod 770 /var/vmail root@mail:/home/amar# chown vmail:mail /var/vmail
Virtual Mail Directory "/var/vmail" using Group "mail" to allow other system's user to manage the content.
Step 9: - Configure Dovecot
Dovecot will manage all the connection for POP and IMAP, local mail directory and receive all incoming emails. Dovecot use to handle authentication for SMTP connection. We also define MySQL database connection string so Dovecot can access all the information from MySQL Database-
9A- Enable Dovecote access to MySQL database
Dovecot will access all the mailbox information including user authentication from Database, Let's make changes in the file - /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
Open dovecot-sql.conf.ext file and add database access as follow
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf.ext
Make the following changes as highlighted below in RED
Save and Exit from File.# Database driver: mysql, pgsql, sqlite
driver = mysql
# Examples:
# connect = host=192.168.1.1 dbname=users
# connect = host=sql.example.com dbname=virtual user=virtual password=blarg
# connect = /etc/dovecot/authdb.sqlite
#
connect = host=localhost dbname=mail user=mail password=mailpassword
# Default password scheme.
#
# List of supported schemes is in
# http://wiki2.dovecot.org/Authentication/PasswordSchemes
#
default_pass_scheme = MD5-CRYPT
# Define the query to obtain a user password.
#
# Note that uid 150 is the "vmail" user and gid 8 is the "mail" group.
#
password_query = \
SELECT username as user, password, '/var/vmail/%d/%n' as userdb_home, \
'maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n' as userdb_mail, 150 as userdb_uid, 8 as userdb_gid \
FROM mailbox WHERE username = '%u' AND active = '1'
# Define the query to obtain user information.
#
# Note that uid 150 is the "vmail" user and gid 8 is the "mail" group.
#
user_query = \
SELECT '/var/vmail/%d/%n' as home, 'maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n' as mail, \
150 AS uid, 8 AS gid, concat('dirsize:storage=', quota) AS quota \
FROM mailbox WHERE username = '%u' AND active = '1'
9B- Make changes in 10-auth.conf file
Dovecot will read the SQL configuration files, we need to enable in 10-auth.conf file lets make changes using below command.
Open 10-auth.conf file and make the changes as follow
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf
Changes are as follows:
# Disable LOGIN command and all other plaintext authentications unless
# SSL/TLS is used (LOGINDISABLED capability). Note that if the remote IP
# matches the local IP (ie. you're connecting from the same computer), the
# connection is considered secure and plaintext authentication is allowed.
disable_plaintext_auth = yes
# Space separated list of wanted authentication mechanisms:
# plain login digest-md5 cram-md5 ntlm rpa apop anonymous gssapi otp skey
# gss-spnego
# NOTE: See also disable_plaintext_auth setting.
auth_mechanisms = plain login
# User database specifies where mails are located and what user/group IDs
# own them. For single-UID configuration use "static" userdb.
#
# <doc/wiki/UserDatabase.txt>
#!include auth-deny.conf.ext
#!include auth-master.conf.ext
#!include auth-system.conf.ext
# Use the SQL database configuration for authentication rather than
# any of these others.
!include auth-sql.conf.ext
#!include auth-ldap.conf.ext
#!include auth-passwdfile.conf.ext
#!include auth-checkpassword.conf.ext
#!include auth-vpopmail.conf.ext
#!include auth-static.conf.ext
Save and Exit from the Files9C- Tell Dovecot where need to store user's mail directory Open 10-mail.conf file and make the changes as follows:
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf
Changes are as follows:# See doc/wiki/Variables.txt for full list. Some examples:
#
# mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
# mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u
# mail_location = mbox:/var/mail/%d/%1n/%n:INDEX=/var/indexes/%d/%1n/%n
#
# <doc/wiki/MailLocation.txt>
#
mail_location = maildir:/var/vmail/%d/%n
# System user and group used to access mails. If you use multiple, userdb
# can override these by returning uid or gid fields. You can use either numbers
# or names. <doc/wiki/UserIds.txt>
mail_uid = vmail
mail_gid = mail
# Valid UID range for users, defaults to 500 and above. This is mostly
# to make sure that users can't log in as daemons or other system users.
# Note that denying root logins is hardcoded to dovecot binary and can't
# be done even if first_valid_uid is set to 0.
#
# Use the vmail user uid here.
first_valid_uid = 150
last_valid_uid = 150
Save and Exit From the file9D- Change Certificates file path
Open 10-ssl.conf file and make the changes as follows:
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf
Make the changes as follows:# SSL/TLS support: yes, no, required. <doc/wiki/SSL.txt>
ssl = yes
# The generated snakeoil certificate:
#ssl_cert = </etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
#ssl_key = </etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# Purchased certificate:
ssl_cert = </etc/ssl/certs/tony.in.crt
ssl_key = </etc/ssl/private/tony.in.key
Save and Exit From the file9E-Modify 10-master.conf
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-master.conf
Make the changes as follows:service auth { # auth_socket_path points to this userdb socket by default. It's typically # used by dovecot-lda, doveadm, possibly imap process, etc. Users that have # full permissions to this socket are able to get a list of all usernames and # get the results of everyone's userdb lookups. # # The default 0666 mode allows anyone to connect to the socket, but the # userdb lookups will succeed only if the userdb returns an "uid" field that # matches the caller process's UID. Also if caller's uid or gid matches the # socket's uid or gid the lookup succeeds. Anything else causes a failure. # # To give the caller full permissions to lookup all users, set the mode to # something else than 0666 and Dovecot lets the kernel enforce the # permissions (e.g. 0777 allows everyone full permissions). unix_listener auth-userdb { mode = 0666 user = vmail group = mail } unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/auth { mode = 0666 # Assuming the default Postfix user and group user = postfix group = postfix }Save and Exit From the file
9F- Change postmaster setting
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/dovecot/conf.d/15-lda.conf
Changes as follows:# Address to use when sending rejection mails.
# Default is postmaster@<your domain>.
postmaster_address = postmaster@tony.in
Save and Exit From the file9G- Change mailbox directory permission
root@mail:/home/amar# chown -R vmail:dovecot /etc/dovecot root@mail:/home/amar# chmod -R o-rwx /etc/dovecot
Step 10: - Configure Antivirus scan and SpamAssassin scan
Amavis, ClamAV, and SpamAssassin are the best tool to scan email, let make the changes as follow to integrate these tools.10A- Add Users
root@mail:/home/amar# adduser clamav amavis Adding user `clamav' to group `amavis' ... Adding user clamav to group amavis Done. root@mail:/home/amar# adduser amavis clamav Adding user `amavis' to group `clamav' ... Adding user amavis to group clamav Done.
10B- Modify configuration file
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/clamav/clamd.conf
Changes as follows:
# Needed to allow things to work with Amavis, when both amavis and clamav
# users are added to one another's groups.
AllowSupplementaryGroups true
10C- Turn on Amavisroot@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/amavis/conf.d/15-content_filter_mode
Changes as followuse strict; # You can modify this file to re-enable SPAM checking through spamassassin # and to re-enable antivirus checking. # # Default antivirus checking mode # Please note, that anti-virus checking is DISABLED by # default. # If You wish to enable it, please uncomment the following lines: @bypass_virus_checks_maps = ( \%bypass_virus_checks, \@bypass_virus_checks_acl, \$bypass_virus_checks_re); # # Default SPAM checking mode # Please note, that anti-spam checking is DISABLED by # default. # If You wish to enable it, please uncomment the following lines: @bypass_spam_checks_maps = ( \%bypass_spam_checks, \@bypass_spam_checks_acl, \$bypass_spam_checks_re); 1; # ensure a defined returnSave and Exit From file
10D- Enable SpamAssassin
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/default/spamassassin
Changes as follow
# Change to one to enable spamd ENABLED=1 # Cronjob # Set to anything but 0 to enable the cron job to automatically update # spamassassin's rules on a nightly basis CRON=1
10E- Enable Database Scan
SpamAssassin under Amavis will only check mail that's determined to be arriving for local delivery. There are a couple of ways to tell Amavis which mails are for local delivery, but here we'll set it up to check the database set up by Postfix Admin. Edit /etc/amavis/conf.d/50-user to look like this:
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/amavis/conf.d/50-user
Changes as follows:
use strict; # # Place your configuration directives here. They will override those in # earlier files. # # See /usr/share/doc/amavisd-new/ for documentation and examples of # the directives you can use in this file # # Three concurrent processes. This should fit into the RAM available on an # AWS micro instance. This has to match the number of processes specified # for Amavis in /etc/postfix/master.cf. $max_servers = 3; # Add spam info headers if at or above that level - this ensures they # are always added. $sa_tag_level_deflt = -9999; # Check the database to see if mail is for local delivery, and thus # should be spam checked. @lookup_sql_dsn = ( ['DBI:mysql:database=mail;host=127.0.0.1;port=3306', 'mail', 'mailpassword']); $sql_select_policy = 'SELECT domain from domain WHERE CONCAT("@",domain) IN (%k)'; # Uncomment to bump up the log level when testing. # $log_level = 2; #------------ Do not modify anything below this line ------------- 1; # ensure a defined return
Save and Exit from file
10E-
Next, make sure the ClamAV database is up to date by running fresh clam. It should be:root@mail:/home/amar# freshclam
10F- Restart services
root@mail:/home/amar# /etc/init.d/spamassassin restart
root@mail:/home/amar# /etc/init.d/clamav-daemon restart
root@mail:/home/amar# /etc/init.d/clamav-daemon restart
root@mail:/home/amar# /etc/init.d/amavis restart
Step 11: - Configure Postfix
Postfix handles incoming mail via the SMTP protocol, and its configuration files have be set up to allow it to integrate with the various other packages we have installed so far. At a high level, we want Postfix to hand off incoming mail to the spam and virus checkers before passing it on to Dovecot for delivery, and to communicate with Dovecot in order to authenticate virtual users who are connecting over SMTP in order to send the email.
11A- Create following files to allow postfix access fo Database.
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_domainaliases_maps.cf
Add following lines
user = mail password = mailpassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail query = SELECT goto FROM alias,alias_domain WHERE alias_domain.alias_domain = '%d' AND alias.address=concat('%u', '@', alias_domain.target_domain) AND alias.active = 1
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_maps.cf
user = mail password = mailpassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = alias select_field = goto where_field = address additional_conditions = and active = '1'
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_domains_maps.cf
user = mail password = mailpassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = domain select_field = domain where_field = domain additional_conditions = and backupmx = '0' and active = '1'
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_domainaliases_maps.cf
user = mail
password = mailpassword
hosts = 127.0.0.1
dbname = mail
query = SELECT maildir FROM mailbox, alias_domain
WHERE alias_domain.alias_domain = '%d'
AND mailbox.username=concat('%u', '@', alias_domain.target_domain )
AND mailbox.active = 1
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_maps.cf
user = mail password = mailpassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail table = mailbox select_field = CONCAT(domain, '/', local_part) where_field = username additional_conditions = and active = '1'
/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_sender_login_maps.cf
user = mail password = mailpassword hosts = 127.0.0.1 dbname = mail query = SELECT goto FROM alias WHERE address='%s'
/etc/postfix/header_checks
/^Received:/ IGNORE
/^User-Agent:/ IGNORE
/^X-Mailer:/ IGNORE
/^X-Originating-IP:/ IGNORE
/^x-cr-[a-z]*:/ IGNORE
/^Thread-Index:/ IGNORE
11B- Modify main.cf file
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
Changes as follows
# See /usr/share/postfix/main.cf.dist for a commented, more complete version # The first text sent to a connecting process. smtpd_banner = $myhostname ESMTP $mail_name biff = no # appending .domain is the MUA's job. append_dot_mydomain = no readme_directory = no # --------------------------------- # SASL parameters # --------------------------------- # Use Dovecot to authenticate. smtpd_sasl_type = dovecot # Referring to /var/spool/postfix/private/auth smtpd_sasl_path = private/auth smtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes broken_sasl_auth_clients = yes smtpd_sasl_security_options = noanonymous smtpd_sasl_local_domain = smtpd_sasl_authenticated_header = yes # --------------------------------- # TLS parameters # --------------------------------- # The default snakeoil certificate. Comment if using a purchased # SSL certificate. smtpd_tls_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem smtpd_tls_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key # Uncomment if using a purchased SSL certificate. # smtpd_tls_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/example.com.crt # smtpd_tls_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/example.com.key # The snakeoil self-signed certificate has no need for a CA file. But # if you are using your own SSL certificate, then you probably have # a CA certificate bundle from your provider. The path to that goes # here. # smtpd_tls_CAfile=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt # Ensure we're not using no-longer-secure protocols. smtpd_tls_mandatory_protocols=!SSLv2,!SSLv3 smtp_tls_note_starttls_offer = yes smtpd_tls_loglevel = 1 smtpd_tls_received_header = yes smtpd_tls_session_cache_timeout = 3600s tls_random_source = dev:/dev/urandom #smtpd_tls_session_cache_database = btree:${data_directory}/smtpd_scache #smtp_tls_session_cache_database = btree:${data_directory}/smtp_scache # Note that forcing use of TLS is going to cause breakage - most mail servers # don't offer it and so delivery will fail, both incoming and outgoing. This is # unfortunate given what various governmental agencies are up to these days. # # Enable (but don't force) all incoming smtp connections to use TLS. smtpd_tls_security_level = may # Enable (but don't force) all outgoing smtp connections to use TLS. smtp_tls_security_level = may # See /usr/share/doc/postfix/TLS_README.gz in the postfix-doc package for # information on enabling SSL in the smtp client. # --------------------------------- # TLS Updates relating to Logjam SSL attacks. # See: https://weakdh.org/sysadmin.html # --------------------------------- smtpd_tls_exclude_ciphers = aNULL, eNULL, EXPORT, DES, RC4, MD5, PSK, aECDH, EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA, EDH-RSA-DES-CDC3-SHA, KRB5-DE5, CBC3-SHA smtpd_tls_dh1024_param_file = /etc/ssl/private/dhparams.pem # --------------------------------- # SMTPD parameters # --------------------------------- # Uncomment the next line to generate "delayed mail" warnings #delay_warning_time = 4h # will it be a permanent error or temporary unknown_local_recipient_reject_code = 450 # how long to keep message on queue before return as failed. maximal_queue_lifetime = 7d # max and min time in seconds between retries if connection failed minimal_backoff_time = 1000s maximal_backoff_time = 8000s # how long to wait when servers connect before receiving rest of data smtp_helo_timeout = 60s # how many address can be used in one message. # effective stopper to mass spammers, accidental copy in whole address list # but may restrict intentional mail shots. smtpd_recipient_limit = 16 # how many error before back off. smtpd_soft_error_limit = 3 # how many max errors before blocking it. smtpd_hard_error_limit = 12 # This next set are important for determining who can send mail and relay mail # to other servers. It is very important to get this right - accidentally producing # an open relay that allows unauthenticated sending of mail is a Very Bad Thing. # # You are encouraged to read up on what exactly each of these options accomplish. # Requirements for the HELO statement smtpd_helo_restrictions = permit_mynetworks, warn_if_reject reject_non_fqdn_hostname, reject_invalid_hostname, permit # Requirements for the sender details. Note that the order matters. # E.g. see http://jimsun.linxnet.com/misc/restriction_order_prelim-03.txt smtpd_sender_restrictions = permit_mynetworks, reject_authenticated_sender_login_mismatch, permit_sasl_authenticated, warn_if_reject reject_non_fqdn_sender, reject_unknown_sender_domain, reject_unauth_pipelining, permit # Requirements for the connecting server smtpd_client_restrictions = reject_rbl_client sbl.spamhaus.org, reject_rbl_client blackholes.easynet.nl # Requirement for the recipient address. Note that the entry for # "check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023" enables Postgrey. smtpd_recipient_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining, permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_non_fqdn_recipient, reject_unknown_recipient_domain, reject_unauth_destination, check_policy_service unix:private/policy-spf, check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023, permit smtpd_data_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining # This is a new option as of Postfix 2.10, and is required in addition to # smtpd_recipient_restrictions for things to work properly in this setup. smtpd_relay_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining, permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_non_fqdn_recipient, reject_unknown_recipient_domain, reject_unauth_destination, check_policy_service unix:private/policy-spf, check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023, permit # require proper helo at connections smtpd_helo_required = yes # waste spammers time before rejecting them smtpd_delay_reject = yes disable_vrfy_command = yes # --------------------------------- # General host and delivery info # ---------------------------------- myhostname = mail.tony.in myorigin = /etc/hostname # Some people see issues when setting mydestination explicitly to the server # subdomain, while leaving it empty generally doesn't hurt. So it is left empty here. # mydestination = mail.example.com, localhost mydestination = # If you have a separate web server that sends outgoing mail through this # mailserver, you may want to add its IP address to the space-delimited list in # mynetworks, e.g. as 10.10.10.10/32. mynetworks = 127.0.0.0/8 [::ffff:127.0.0.0]/104 [::1]/128 mailbox_size_limit = 0 recipient_delimiter = + inet_interfaces = all mynetworks_style = host # This specifies where the virtual mailbox folders will be located. virtual_mailbox_base = /var/vmail # This is for the mailbox location for each user. The domainaliases # map allows us to make use of Postfix Admin's domain alias feature. virtual_mailbox_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_maps.cf, mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_mailbox_domainaliases_maps.cf # and their user id virtual_uid_maps = static:150 # and group id virtual_gid_maps = static:8 # This is for aliases. The domainaliases map allows us to make # use of Postfix Admin's domain alias feature. virtual_alias_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_maps.cf, mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_alias_domainaliases_maps.cf # This is for domain lookups. virtual_mailbox_domains = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_domains_maps.cf # Used in conjunction with reject_authenticated_sender_login_mismatch to # verify that the sender is sending with their own address, or with one # of the aliases mapped to that address. smtpd_sender_login_maps = mysql:/etc/postfix/mysql_virtual_sender_login_maps.cf # --------------------------------- # Integration with other packages # --------------------------------------- # Tell postfix to hand off mail to the definition for dovecot in master.cf virtual_transport = dovecot dovecot_destination_recipient_limit = 1 # Use amavis for virus and spam scanning content_filter = amavis:[127.0.0.1]:10024 # Settings for checking SPF to cut down spam. policy-spf_time_limit = 3600s # --------------------------------- # Header manipulation # -------------------------------------- # Getting rid of unwanted headers. See: https://posluns.com/guides/header-removal/ header_checks = regexp:/etc/postfix/header_checks enable_original_recipient = no # getting rid of x-original-to
Save and exit from file
11C- Modify master.cf
root@mail:/home/amar# vi /etc/postfix/master.cf
Changes as follows
# Postfix master process configuration file. For details on the format # of the file, see the master(5) manual page (command: "man 5 master" or # on-line: http://www.postfix.org/master.5.html). # # Do not forget to execute "postfix reload" after editing this file. # # ========================================================================== # service type private unpriv chroot wakeup maxproc command + args # (yes) (yes) (no) (never) (100) # ========================================================================== smtp inet n - y - - smtpd #smtp inet n - y - 1 postscreen #smtpd pass - - y - - smtpd #dnsblog unix - - y - 0 dnsblog #tlsproxy unix - - y - 0 tlsproxy # SMTP with TLS on port 587. Currently commented. #submission inet n - y - - smtpd # -o syslog_name=postfix/submission # -o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt # -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes # -o smtpd_enforce_tls=yes # -o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject_unauth_destination,reject # -o smtpd_sasl_tls_security_options=noanonymous # SMTP over SSL on port 465. smtps inet n - y - - smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/smtps -o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes -o smtpd_tls_auth_only=yes -o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject_unauth_destination,reject -o smtpd_sasl_security_options=noanonymous,noplaintext -o smtpd_sasl_tls_security_options=noanonymous #628 inet n - y - - qmqpd pickup unix n - y 60 1 pickup cleanup unix n - y - 0 cleanup qmgr unix n - n 300 1 qmgr #qmgr unix n - n 300 1 oqmgr tlsmgr unix - - y 1000? 1 tlsmgr rewrite unix - - y - - trivial-rewrite bounce unix - - y - 0 bounce defer unix - - y - 0 bounce trace unix - - y - 0 bounce verify unix - - y - 1 verify flush unix n - y 1000? 0 flush proxymap unix - - n - - proxymap proxywrite unix - - n - 1 proxymap smtp unix - - y - - smtp relay unix - - y - - smtp # -o smtp_helo_timeout=5 -o smtp_connect_timeout=5 showq unix n - y - - showq error unix - - y - - error retry unix - - y - - error discard unix - - y - - discard local unix - n n - - local virtual unix - n n - - virtual lmtp unix - - y - - lmtp anvil unix - - y - 1 anvil scache unix - - y - 1 scache # # ==================================================================== # Interfaces to non-Postfix software. Be sure to examine the manual # pages of the non-Postfix software to find out what options it wants. # # Many of the following services use the Postfix pipe(8) delivery # agent. See the pipe(8) man page for information about ${recipient} # and other message envelope options. # ==================================================================== # # maildrop. See the Postfix MAILDROP_README file for details. # Also specify in main.cf: maildrop_destination_recipient_limit=1 # maildrop unix - n n - - pipe flags=DRhu user=vmail argv=/usr/bin/maildrop -d ${recipient} # # ==================================================================== # # Recent Cyrus versions can use the existing "lmtp" master.cf entry. # # Specify in cyrus.conf: # lmtp cmd="lmtpd -a" listen="localhost:lmtp" proto=tcp4 # # Specify in main.cf one or more of the following: # mailbox_transport = lmtp:inet:localhost # virtual_transport = lmtp:inet:localhost # # ==================================================================== # # Cyrus 2.1.5 (Amos Gouaux) # Also specify in main.cf: cyrus_destination_recipient_limit=1 # #cyrus unix - n n - - pipe # user=cyrus argv=/cyrus/bin/deliver -e -r ${sender} -m ${extension} ${user} # # ==================================================================== # Old example of delivery via Cyrus. # #old-cyrus unix - n n - - pipe # flags=R user=cyrus argv=/cyrus/bin/deliver -e -m ${extension} ${user} # # ==================================================================== # # See the Postfix UUCP_README file for configuration details. # uucp unix - n n - - pipe flags=Fqhu user=uucp argv=uux -r -n -z -a$sender - $nexthop!rmail ($recipient) # # Other external delivery methods. # ifmail unix - n n - - pipe flags=F user=ftn argv=/usr/lib/ifmail/ifmail -r $nexthop ($recipient) bsmtp unix - n n - - pipe flags=Fq. user=bsmtp argv=/usr/lib/bsmtp/bsmtp -t$nexthop -f$sender $recipient scalemail-backend unix - n n - 2 pipe flags=R user=scalemail argv=/usr/lib/scalemail/bin/scalemail-store ${nexthop} ${user} ${extension} mailman unix - n n - - pipe flags=FR user=list argv=/usr/lib/mailman/bin/postfix-to-mailman.py ${nexthop} ${user} # The next two entries integrate with Amavis for anti-virus/spam checks. amavis unix - - y - 3 smtp -o smtp_data_done_timeout=1200 -o smtp_send_xforward_command=yes -o disable_dns_lookups=yes -o max_use=20 127.0.0.1:10025 inet n - y - - smtpd -o content_filter= -o local_recipient_maps= -o relay_recipient_maps= -o smtpd_restriction_classes= -o smtpd_delay_reject=no -o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject -o smtpd_helo_restrictions= -o smtpd_sender_restrictions= -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,reject -o smtpd_data_restrictions=reject_unauth_pipelining -o smtpd_end_of_data_restrictions= -o mynetworks=127.0.0.0/8 -o smtpd_error_sleep_time=0 -o smtpd_soft_error_limit=1001 -o smtpd_hard_error_limit=1000 -o smtpd_client_connection_count_limit=0 -o smtpd_client_connection_rate_limit=0 -o receive_override_options=no_header_body_checks,no_unknown_recipient_checks,no_milters # Integration with Dovecot - hand mail over to it for local delivery, and # run the process under the vmail user and mail group. dovecot unix - n n - - pipe flags=DRhu user=vmail:mail argv=/usr/lib/dovecot/dovecot-lda -d $(recipient) # Integration with the SPF check package. policy-spf unix - n n - - spawn user=nobody argv=/usr/bin/policyd-spf
Step 12- Restart all the services:
root@mail:/home/amar# service postfix restart root@mail:/home/amar# service spamassassin restart root@mail:/home/amar# service clamav-daemon restart root@mail:/home/amar# service amavis restart root@mail:/home/amar# service dovecot restart
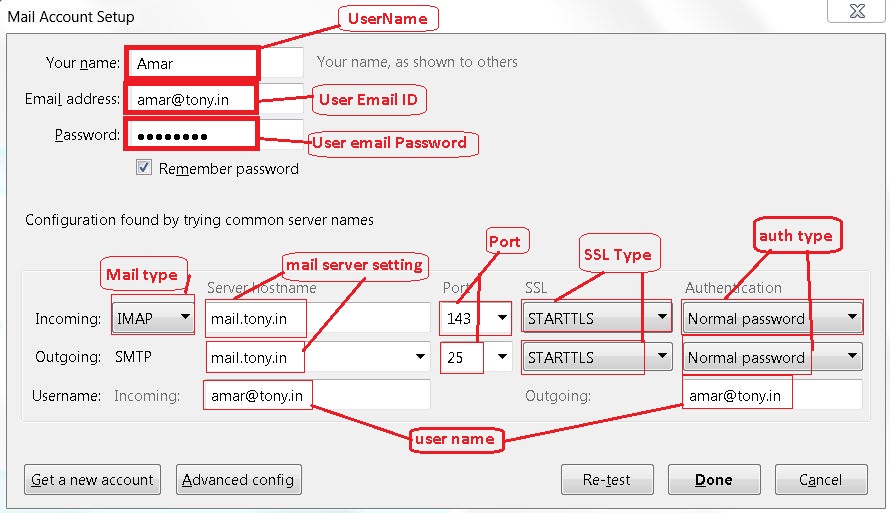
Use above settings to configure E-mail Client.
Step 14- Setup SPF (Sender Policy Framework):
Example 1 Allow mail from all hosts listed in the MX records for the domain:
Step 14- Setup SPF (Sender Policy Framework):
Example 1 Allow mail from all hosts listed in the MX records for the domain:
v=spf1 mx -all
Example 2 Allow mail from a specific host:v=spf1 a:mail.example.com -all
Add the SPF policy agent to Postfix:
Install following package first.
# apt install postfix-policyd-spf-python postfix-pcre
/etc/postfix-policyd-spf-python/policyd-spf.conf to change the HELO_reject and Mail_From_rejectsettings to False. root@mail:~# vi /etc/postfix-policyd-spf-python/policyd-spf.conf
Your file looks like below:
debugLevel = 1 TestOnly = 1 HELO_reject = False Mail_From_reject = False PermError_reject = False TempError_Defer = FalseSave and exit from file
2- Edit /etc/postfix/master.cf and add the following line
policyd-spf unix - n n - 0 spawn
user=policyd-spf argv=/usr/bin/policyd-spf
Save and exit from file3-Edit
/etc/postfix/main.cf and add the following line to increase postfix agent policy timeoutpolicyd-spf_time_limit = 3600
4- Edit /etc/postfix/main.cfand change smtpd_recipient_restrictions listsmtpd_recipient_restrictions = reject_unauth_pipelining, permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, reject_non_fqdn_recipient, reject_unknown_recipient_domain, reject_unauth_destination, check_policy_service unix:private/policy-spf, check_policy_service inet:127.0.0.1:10023, permit
Save and exit from file
5-Restart Postfixroot@mail:~# systemctl restart postfix
!!!Our E-Mail Server has been configured successfully!!!










This is really great work. Thanks!
ReplyDeleteand Telegram : salimrezabd1
DeleteDo you need powermta?
Thanks very much for such a clear, detailed tutorial.
ReplyDeleteThe only change I made was to install the official Debian package, which is now the same version.
Everything works OK.
This was truly awesome. thanks so much for this!! AWS Online Training
ReplyDeletecan we store message in MySQL database or just we store user id and there password
ReplyDeleteWell written technical blog. your step by step guide to choose the best linux mail server is great. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteGood tutorial
ReplyDeletebuy bulk smtp server
buy powermta
buy smtp server with bitcoin
class 9 tution classes in gurgaon
ReplyDeleteBest Indian Travel Agency Database For Business And Marketing
ReplyDeleteBest blog ever i read on such a great topic mattress cleaning service
ReplyDelete🖐 Bro, I have old to latest, almost all version of PowerMTA + snmp, api, and proxy supported. with lifetime license key
ReplyDelete🙏🙏If you want/need, please contact me.👇
skype ac: salimrezabd04
or telegram: salimrezabd1
or telegram: salimrezabd